Book
Appointments
in Advance
Let our specialist talk to you
Home » Dental Cavity
Dental cavity
Overview
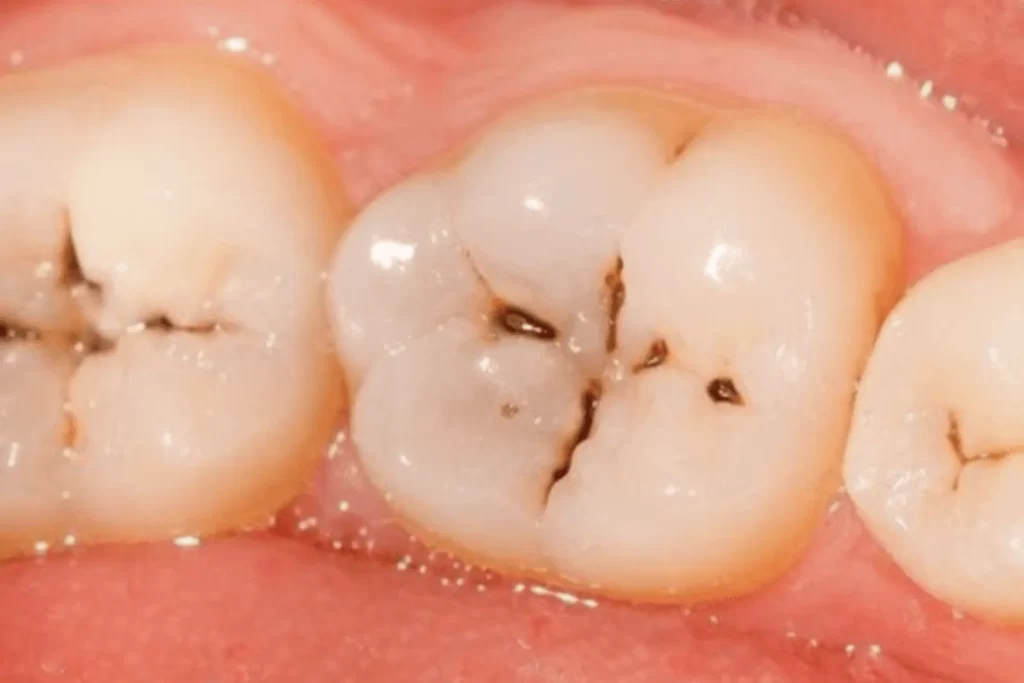
A dental cavity, also known as tooth decay or dental caries, is a condition in which bacteria in the mouth produce acid that erodes the hard outer layer (enamel) of a tooth, causing a hole or cavity to form. Cavities are one of the most common dental problems and can occur at any age.
If left untreated, dental cavities can lead to more serious dental problems, such as infections, abscesses, or even tooth loss. In addition, the decay can spread to other teeth, leading to further dental problems.
Causes
Dental cavities are caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Bacteria in the mouth: The bacteria in the mouth form a sticky film called plaque, which can build up on teeth and produce acids that can eat away at the tooth’s enamel.
- Sugary and starchy foods: Foods that are high in sugar and starch can contribute to the formation of plaque and the production of acids that can lead to cavities.
- Poor oral hygiene: Failing to brush and floss regularly can allow plaque to build up on teeth, increasing the risk of cavities.
- Dry mouth: A lack of saliva can contribute to the formation of cavities by reducing the mouth’s ability to neutralize acids and wash away food particles.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a dental cavity may vary depending on the severity of the decay. Common symptoms include:
- Tooth sensitivity or pain
- Visible holes or pits in the teeth
- Discoloration or staining of the teeth
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks
Diagnosis
To diagnose a dental cavity, a dentist will perform a visual examination of the teeth and may also take x-rays to assess the extent of the decay.
Treatment
The treatment for a dental cavity depends on the extent of the decay. Some treatment options include:
- Fillings: A filling is a common treatment for cavities. The decayed portion of the tooth is removed, and the cavity is filled with a material such as amalgam or composite resin.
- Crowns: If the cavity is large or the tooth is weakened, a crown may be necessary to protect the tooth and restore its function.
- Root Canal Treatment: If the decay has reached the tooth’s pulp or nerve, a root canal may be necessary to remove the damaged tissue and save the tooth.
- Extraction: If the tooth is severely damaged or cannot be saved, the tooth may need to be extracted.
Prevention
Preventing dental cavities involves maintaining good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting a dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. Other preventive measures include limiting sugary and starchy foods, using fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash, and addressing any underlying dental issues, such as dry mouth or gum disease, promptly.
Start Your Treatment Now
Our specialist for
Cavity Concern

Dr. Naveena Ponnada
Associate Surgeon -
Restorative Dentist & Micro-Endodontist
BDS, MDS - Restorstive Dentist & Micro-Endodontist
6+ Years of Experience
Speciality:
Root Canal Treatment, Re-Root Canal Treatment, Microscopic Root Canal, Tooth Filling, Tooth Fracture, Tooth Sensitivity, Teeth Whitening, Crowns, Dental Veneers, Surgical & Non-Surgical RCTs.

Dr. Charu Sonegare
Associate Surgeon - Restorative Dentist & Micro - Endodontist
BDS, MDS - Restorstive Dentist & Micro-Endodontist
3+ Years of Experience
Speciality:
Root Canal Treatment, Re-Root Canal Treatment, Tooth Filling, Teeth Whitening, Crowns, Veneers and Surgical & Non- Surgical RCTs

